Reminder: we will have an exam review tomorrow (Saturday) at 8:30 am. Below is the link to the power points given during todays lecture.
http://faculty.weber.edu/choagstrom/PIGuestLectureSpring2013.pdf
Zoology Principles I
Friday, April 19, 2013
Wednesday, April 17, 2013
Match up the terms below with their definitions - try to come up with an example of each term
Terms
- Phylogeny
- Ancestral
- Commensalism
- Taxonomy
- Character Displacement
- Demography
- Mutualism
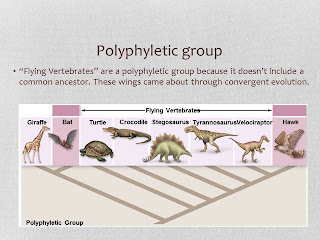
- Polyphyletic
- Derived
- Convergent Evolution
- Embryology
- Mullerian Mimicry
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Paraphyletic
- Doubling Time
- Batesian Mimicry
- Carrying Capacity
- Systematics
- Cladistics
- Co-evolution
- Resource Partitioning
- Homologous structure
- Monophyletic
- Character Release
- Aposematic coloration
- Analogous structure
Definitions
| 1. The time it takes for a population to double |
| 2. The subdivision of a niche by 2 closely related population in order to avoid competition with each other |
| 3. A field of study that argues taxonomy must reflect the true evolutionary history |
| 4. A characteristic that is found in 2 or more animals that have the same function but is not found in a common ancestor |
| |
7. A way of classifying, categorizing and naming organisms
|
| 9. A signal that has evolved to warn predators that the animal is deadly, dangerous, or distasteful | |
other is negatively affected |
|
| 15. The study of early animal development | |
environment | |
| 18. The evolutionary history and line of descent of a species | |
| 19. Morphological feature becomes more similar between closely related species when geographically isolated |
| 20. A type of Symbiosis in which one species benefits from the relationship and the other is not affected |
21. The study of populations, originally termed for the study of human populations
|
Monday, April 1, 2013
Vocabulary for Exam 3
This is a list of vocabulary that I thought might be important for exam 3. Most of them are on the exam review (posted before this and still available) but some are not. Let me know if you don't know some of these.
·
Inheritance of Acquired characteristics
·
Transformation
·
Stasis
·
Spontaneous generation
·
Transmutation
·
Darwins Observations – you should know where he went, what he saw, what he thought about these observations
·
Theories of Natural Selection
·
Natural Selection
·
Variational Evolution
·
Special creation
·
Struggle for existence
·
Industrial melanism
·
Directional selection
·
Stabilizing selection
·
Disruptive selection
·
Artificial selection
·
Physiological adaptation
·
Phenotypic plasticity
·
Genetic drift
·
Intrasexual selection
·
Intersexual selection
·
Sexual dimorphism
·
Polyandrous
·
Hamilton Zuk Hypothesis
·
Handicap Hypothesis
·
Runaway selection
·
Primary sex characteristics
·
Secondary sex characteristics
·
Sexy Son Hypothesis
·
Polymorphism
·
Sibling species
·
Subspecies
·
Character Displacement
·
Character Release
·
Sympatric
·
Allopatric
·
Sympatric Speciation
·
Allopatric Speciation
·
Prezygotic Isolation
·
Geographic isolation
·
Ecological isolation
·
Behavioral isolation
·
Temporal isolation
·
Mechanical isolation
·
Gametic isolation
·
Post zygotic isolation
·
Zygote death
·
Infertility
·
Genus species
·
Founder effect
·
Genetic drift
·
Bottleneck
·
Adaptive radiation
·
Reinforcement
·
Ring species
·
Host shift
Sunday, March 31, 2013
Exam 3 review
** Wherever it has (CATA) following a question it means circle all that apply. Good luck!!
1.
In a population
of fish large males that are able to effectively defend a breeding zone are
selected for by the females in the population. Intermediate sized males are
unable to defend a breeding zone and are not usually picked by the females.
Small males in this population look a lot like the females and are often
ignored when they enter the breeding zone of a large male allowing them to
“sneak fertilize” the eggs left by the female. After a period of time the
population shows increased quantities of both large and small male fish.
a.
What mode of
selection is occurring?
i. Directional Selection
ii. Stabilizing Selection
iii. Artificial Selection
iv. Natural Selection
v. Disruptive Selection
b.
T/F – This is
an example of sexual selection? If true what type? _______________________________
2.
A small number
of birds are blown from the mainland to an uninhabited island. The parent
population had many different variations of feather color but the new much
smaller island population only shows 2 distinct color differences, blue and
red. The island has two endemic tree species that drop seeds throughout the
year, and the seeds dropped range from 1 cm to 4 cm. After a long period of
time passes the bird populations are evaluated and several different sympatric
populations are observed. Population (A) has large beaks and has both blue and
red individuals that don’t select for color when mating. Population (B) has
very small beaks and only blue individuals that forage for food during the
evening. Population (C) eats early in the morning, has bright red males that
sing during breeding season, and brown/red females. A researcher watches the
population through an entire breeding season and finds that none of the
populations interbreed.
a.
What describes
the initial event that occurred? ______________. This is an example of genetic
_______.
b.
What describes
the phenotypic variation in population A? ___________________________
c.
What describes
the phenotypic variation in population C? ________________________________
d.
What term
describes the beak differences between population A and B? ___________________________
e.
What mode of
selection occurred with the beaks in population A? ________________________________
f.
What isolating
mechanism keeps population B and C from interbreeding? ________________________
g.
T/F – The trees
on the island also live on the mainland making a great food source for the
birds
3.
A population of
Elk has males that compete for breeding rights with the females in the herd.
After many generations it is observed that the breeding males have considerably
larger antlers than the nonbreeding males. After considerable time has passed
the males are observed to have extremely large antlers that could potentially
inhibit foraging behavior but are still selected for by the females.
a.
T/F this
species exhibits polyandry.
b.
The competition
occurring between the males is an example of __________________________
c.
The extremely
large antlers are an example of _____________________________
d.
What idea explains
the increased survivability of males with extremely large antlers? _________________
e.
What type of
characteristic are the male Elk antlers? ___________________________________
4.
Match up the
following: match a name (a-e) with a description (f-j)
a.
Malthus
b.
LaMarck
c.
Darwin
d.
Mayr
e.
Wallace
f.
I developed the
Biological Species Concept
g.
I studied
populations in South East Asia and proposed Natural Selection as the mechanism
of Evolution
h.
I wrote “An
Essay on Population” and inspired the idea that individuals struggle for existence
i.
I studied
individual variation within populations and proposed Natural Selection as the
mechanism of Evolution
j.
I studied
individual variation within populations and proposed Transmutation as the
mechanism of Evolution
5. “Superbugs” that
evolved from the overuse of antibiotics is an example of:
a. Natural
Selection
b. Transformation
c. Special
Creation
d. Artificial
Selection
6. T/F – Ring
species are good evidence of Evolution
7. Variational
Evolution is a synonym for:
a. Special
Creation
b. Natural
Selection
c. Transmutation
d. Disruptive
Selection
8. Prezygotic
Isolating mechanisms include: (CATA)
a. Geographical
Barriers
b. Infertility
c. 1° sex
characteristic incompatibility
d. Gametic
9. T/F – Sibling
species would be considered 2 separate species according to the Biological
Species Concept.
10. Character
Release occurs with species that are: (CATA)
a. Sympatric
b. Temporally
Isolated
c. Allopatric
d. Phenotypically
similar
11. Human birth
weight is a good example of: (CATA)
a. Stabilizing
Selection
b. Directional
Selection
c. Polymorphism
d. Disruptive
Selection
12. T/F – Darwin
and Lamarck proposed the Theory of Natural Selection in 1959.
13. What idea
proposes: individuals with brighter colors have better health
a. Hamilton Zuk
Hypothesis
b. Sexy Son
Hypothesis
c. Handicap
Hypothesis
14. A set of twins
are predisposed to develop Type II Diabetes. Twin A doesn’t exercise and eats
high sugar high fat foods throughout his life. Twin B exercises and eats
healthy through his life. Twin A develops diabetes and twin B does not. This is
an example of ____________ (CATA)
a. Dimorphism
b. Polymorphism
c. Phenotypic
Plasticity
d. Character
Displacement
15. Cricket
populations that don’t interbreed due to chirp rate differences show what type
of isolation? (CATA)
a. Temporal
b. Ecological
c. Behavioral
d. Mechanical
16. T/F – 2
sympatric species occupy the same niche.
17. An individual
in a population can __________? (CATA)
a. Live
b. Change
c. Adapt
d. Die
18. Inheritance of
Acquired Characteristics involves: (CATA)
a. Variational
Evolution
b. Trasformational
Evolution
c. Physiological
Adaptation
d. Stasis
e. Individual
Adaptation
19. T/F – Ecological Isolation prevents different
species from interbreeding in part because they eat different kinds of food.
20. Natural
Selection drives ________ (CATA)
a. Character
Displacement
b. Adaptive
radiation
c. Transformational
Evolution
d. Allopatric
Speciation
21. A man and a
woman living in New Orleans have a low red blood cell count. They move to Alta
UT and after a year notice that their red blood cell count is considerably
higher than before. The woman gives birth and the child’s red blood cell count
is also high. This is an example of _________ (CATA)
a. Transmutation
b. Physiological
adaptation
c. Character
Displacement
d. Inheritance of
Acquired Characteristics
22. Which of the
following is a post zygotic reproductive isolating mechanism? (CATA)
a. Behavioral
b. Infertility
c. Fetal Death
d. Geographical
Barriers
e. Reinforcement
23. Which mechanism
of reproductive isolation is not controlled by genes? (CATA)
a. Behavioral
b. Geographical
Barriers
c. Temporal
d. Mechanical
e. Gametic
24. T/F –
Subspecies are phenotypically diverse and sympatric
25. Which of the
following were important points of Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection? (CATA)
a. “Special
Creation” was rejected
b. Humans evolved
through the same mechanism as all other living things
c. Variational
Evolution – individuals don’t change, only populations change
d. Natural
Selection is “goal less”
26. T/F – Sympatric
speciation relies on physical barriers to separate individuals of a population.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)